Introduction
While architecting cloud-native applications, you need to ensure that your system is highly available, performant, scalable, fault-tolerant, and has the capability to recover from a disaster scenario. In this article, Samir Behara discusses the options available when designing the database architecture to achieve scalability.
For further detail, reading see an article on Reg Gate
In this post, I will explain how we can deploy highly scalable PostgresSQL databases using Docker. Also, I will talk about how to connect our microservices (based on Spring Boot) with scaled database deployments via api gateway by using practical examples.
Example Scenario
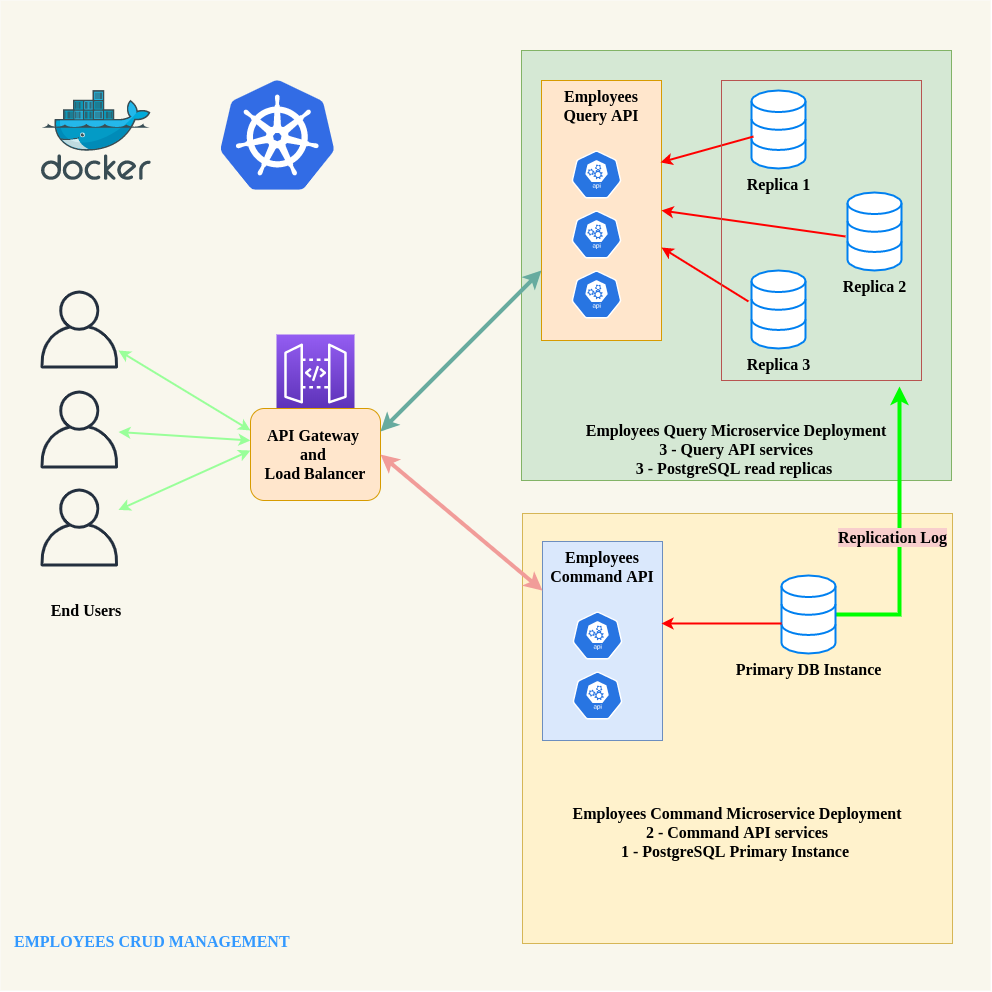
Query APIs - on Github
@Bean
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> employeeRoutes(EmployeeHandler handler) {
return route(GET("/employees/{id}").and(accept(APPLICATION_JSON)), handler::getEmployee)
.andRoute(GET("/employees").and(accept(APPLICATION_JSON)), handler::listEmployee);
}
Command APIs - on Github
@Bean
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> employeeRoutes(EmployeeHandler handler) {
return route(DELETE("/employees/{id}").and(accept(APPLICATION_JSON)), handler::deleteEmployee)
.andRoute(PUT("/employees/{id}").and(accept(APPLICATION_JSON)), handler::updateEmployee)
.andRoute(POST("/employees").and(accept(APPLICATION_JSON)), handler::createEmployee);
}
API Gateway with KrakenD - on Github
KrakenD is a stateless, distributed, high-performance API Gateway that helps you effortlessly adopt microservices. The configuration file for KrakenD to address our requirements:
{
"version": 2,
"endpoints": [
{
"endpoint": "/v1/employees",
"method": "GET",
"backend": [
{
"url_pattern": "/employees",
"method": "GET",
"host": ["http://query:8080"]
}
]
},
{
"endpoint": "/v1/employees/{id}",
"method": "GET",
"backend": [
{
"url_pattern": "/employees/{id}",
"method": "GET",
"host": ["http://query:8080"]
}
]
},
{
"endpoint": "/v1/employees",
"method": "POST",
"backend": [
{
"url_pattern": "/employees",
"method": "POST",
"host": ["http://command:8080"]
}
]
},
{
"endpoint": "/v1/employees/{id}",
"method": "DELETE",
"backend": [
{
"url_pattern": "/employees/{id}",
"method": "DELETE",
"host": ["http://command:8080"]
}
]
},
{
"endpoint": "/v1/employees/{id}",
"method": "PUT",
"backend": [
{
"url_pattern": "/employees/{id}",
"method": "PUT",
"host": ["http://command:8080"]
}
]
}
],
"extra_config": {}
}
Docker Stack - on Github
You can define number of replicas as you need for high scalable database design.
...
services:
# -------------------------------------------------
# Application Backend Databases
# -------------------------------------------------
replica:
...
deploy:
replicas: 3
...
primary:
...
deploy:
replicas: 1
...
# -------------------------------------------------
# Api Gateway
# -------------------------------------------------
gateway:
...
deploy:
replicas: 1
...
# -------------------------------------------------
# Applications
# -------------------------------------------------
command:
...
deploy:
replicas: 1
...
query:
...
deploy:
replicas: 1
...
ui:
...
deploy:
replicas: 1
...
Deploy in Docker Swarm
Let’s build the docker images that needed on this scenario. Firstly, clone the github repo and checkout the branch 13-highly-scalable-database-designs then run following commands:
make build && docker-compose build --no-cache
To enable a docker swarm in your machine:
docker swarm init
To deploy using docker-compose.stack.yml
docker stack deploy --compose-file docker-compose.stack.yml highly-scalable-db
Testing APIs
For testing, we need a host and port for api gateway. The default port for api gateway is 8080, so to identify a host ip address lets run docker network inspect command for gateway.
docker network inspect highly-scalable-db_gateway | grep 'IP\"'
export API_HOST=<IP Address>
export API_HOST_PORT=8080
Install httpie tool on your machine. Install Documentation
Create New Employee
http POST $API_HOST:$API_HOST_PORT/v1/employees name="Bhuwan Prasad Upadhyay"
List Employees
http $API_HOST:$API_HOST_PORT/v1/employees
Get Employee by Id
http $API_HOST:$API_HOST_PORT/v1/employees/<employeeId>
Update an Employee
http PUT $API_HOST:$API_HOST_PORT/v1/employees/<employeeId> name="Bandana Poudyal"
Delete an Employee
http DELETE $API_HOST:$API_HOST_PORT/v1/employees/<employeeId>
