Introduction
Security and working with secrets is a concern of every developer working with databases, user credentials or API keys. Vault steps in by providing a secure storage combined with access control, revocation, key rolling and auditing. In short: Vault is a service for securely accessing and storing secrets.
In this post, I’ll walk you through to store secrets into vault for your application.
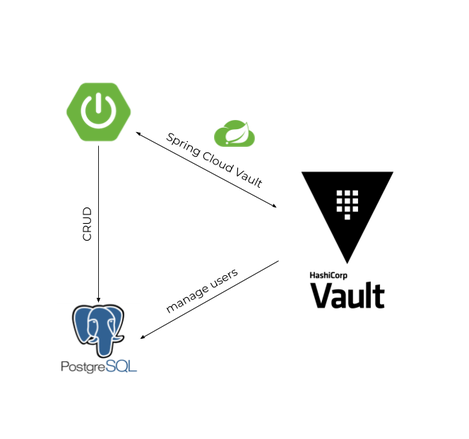
You’ll learn how to setup Spring Cloud Vault to store and read database credentials for your stand-alone application from vault.
Start PostgreSQL and Vault locally
You can download docker-compose.yml file and just run the following to get PostgreSQL and Vault started locally in docker containers.
docker-compose up -d
Creating the VAULT PostgreSQL credentials
Let’s access vault container in your terminal.
docker exec -it example-vault /bin/sh
export VAULT_TOKEN="00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
export VAULT_ADDR="http://127.0.0.1:8200"
Once you have access to vault and postgres access, do the following to enable postgres and create a role that the application will use to connect to PostgreSQL.
- Enable secrets for postgresql
vault secrets enable postgresql
- Write postgresql connection url
vault write postgresql/config/connection \
connection_url="postgresql://user:password@example-vault-db:5432/postgres?sslmode=disable"
- Apply lease setting: vault create new username and password for database
vault write postgresql/config/lease lease=1h lease_max=24h
- Add role for user in database
vault write postgresql/roles/readonly \
sql="CREATE ROLE \"{{name}}\" WITH LOGIN PASSWORD '{{password}}' VALID UNTIL '{{expiration}}';
GRANT ALL ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO \"{{name}}\";"
- To generate new set of credentials run (Vault is now configured to create and manage credentials for Postgres!)
vault read postgresql/creds/readonly
Output
Key Value
--- -----
lease_id postgresql/creds/readonly/ihWk1Q9cC3uHgjFBYOBJZFTv
lease_duration 1h
lease_renewable true
password 4878ef62-ed3d-098e-22c7-71af6891eaa8
username token-954d49c2-9269-451d-9ce9-97e5aa887222
For more info visit vault documentation here: PostgreSQL Secret Engines
Create a Spring Boot Project
curl https://start.spring.io/starter.tgz -d dependencies=postgresql,cloud-starter-vault-config,data-jpa \
-d groupId=io.github.bhuwanupadhyay \
-d artifactId=example-vault \
-d packageName=io.github.bhuwanupadhyay.tutorial \
-d baseDir=example-vault \
-d bootVersion=2.2.2.RELEASE | tar -xzvf -
cd example-vault
Using VAULT in Spring Boot Project with Spring Cloud
Needed maven dependencies under you maven project pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-vault-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-vault-config-databases</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
The spring cloud use bootstrap.yml or bootstrap.properties file. So, to connect with vault you need to define following values in bootstrap.yml file.
spring:
application:
name: example-vault
cloud:
vault:
uri: http://localhost:8200
token: '00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000'
database:
enabled: true
role: readonly
backend: postgresql
datasource:
url: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/postgres
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: create-drop
Database Access: PostgreSQL (read/write)
Let’s implement customer entity and its spring data repository as follows:
Entity
@Entity
public class Customer {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String name;
public Customer() {
}
public Customer(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Customer customer = (Customer) o;
return Objects.equals(id, customer.id);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id);
}
}
Entity Data Repository
public interface CustomerRepository extends JpaRepository<Customer, Long> {
}
Test Scenario
@Spring BootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private CustomerRepository repository;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
repository.deleteAll();
}
@Test
void canAddCustomer() {
String name = "Vault - " + UUID.randomUUID().toString();
repository.save(new Customer(name));
assertEquals(name, repository.findAll().get(0).getName());
}
}
You can find example on github: Source Code
