477 words
2 minutes
JPA Model for Document Structure Entity
Introduction
JPA Model for Document Structure Entity.
Before software can be reusable it first has to be usable.
— Ralph Johnson
In SQL, sometimes you want to store directly JSON documents without creating a relational table (like MongoDB or key-value pair). JSON documents support embedded fields, so related data and lists of data can be stored with the document instead of an external table.
In this snippet, you’ll find how to map a JSON document structure model in JPA without having a direct relational table.
Step 1: Define Entity
Document structure of employee entity that has enum, collection, map, nested object, and nested collection. 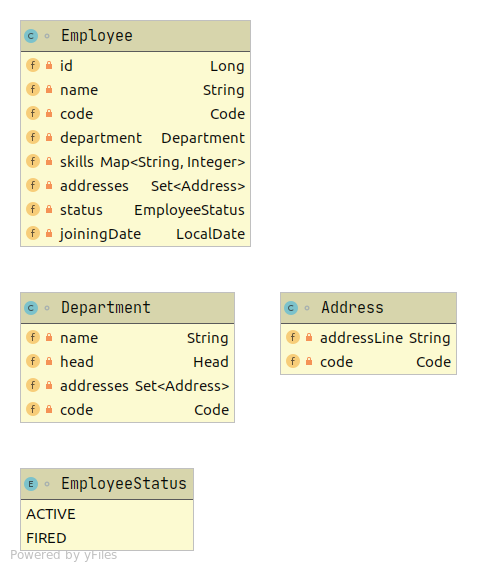
Step 2: Model entity for JPA
enum EmployeeStatus {
ACTIVE, FIRED
}
@Embeddable
@Access(AccessType.FIELD)
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode
@ToString
class Head {
private String name;
@Embedded
private Code code;
}
@Embeddable
@Access(AccessType.FIELD)
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode
@ToString
class Department {
private String name;
private Head head;
@ElementCollection(fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
private Set<Address> addresses;
@Embedded
private Code code;
}
@Embeddable
@Access(AccessType.FIELD)
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode
@ToString
class Code {
private String code;
}
@Embeddable
@Access(AccessType.FIELD)
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode
@ToString
class Address {
private String addressLine;
@Embedded
private Code code;
}
@Entity
@Table(name = "EMPLOYEES")
@Access(AccessType.FIELD)
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
@EqualsAndHashCode(of = "id")
@ToString(of = "id")
class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
@Embedded
private Code code;
@Embedded
private Department department;
@ElementCollection(fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
private Map<String, Integer> skills;
@ElementCollection(fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
private Set<Address> addresses;
@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
private EmployeeStatus status;
private LocalDate joiningDate;
public Employee(String name,
Department department,
Map<String, Integer> skills,
Set<Address> addresses,
Code code) {
this.name = name;
this.department = department;
this.skills = skills;
this.addresses = addresses;
this.joiningDate = LocalDate.now();
this.status = EmployeeStatus.ACTIVE;
this.code = code;
}
}
Step 3: JPA Repository
interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Long> {
}
Step 4: Application Properties
To support JPA Multiple Embedded fields with a prefix without having @AttributeOverride annotations:
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming.implicit-strategy=org.hibernate.boot.model.naming.ImplicitNamingStrategyComponentPathImpl
Step 4: Usage
@Spring BootApplication
@EnableJpaRepositories(considerNestedRepositories = true)
@Slf4j
public class JPAModelForDocumentStructureEntity {
private final EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
public JPAModelForDocumentStructureEntity(EmployeeRepository employeeRepository) {
this.employeeRepository = employeeRepository;
}
@EventListener
public void run(ApplicationReadyEvent readyEvent) {
Map<String, Integer> skills = new HashMap<>();
skills.put("Java", 90);
skills.put("Python", 80);
Address addressLine1 = new Address("addressLine1", new Code("1-CODE"));
Address addressLine2 = new Address("addressLine2", new Code("2-CODE"));
Set<Address> addresses1 = Set.of(addressLine1, addressLine2);
Set<Address> addresses2 = Set.of(addressLine1, addressLine2);
Head head = new Head("h-name", new Code("H-CODE"));
Department department = new Department("d-name", head, addresses1, new Code("D-CODE"));
Employee employee = new Employee("e-name", department, skills, addresses2, new Code("E-CODE"));
// Save
Employee saved = employeeRepository.save(employee);
// Find by Id
Employee findById = employeeRepository.findById(saved.getId()).get();
log(findById);
}
private void log(Employee employee) {
log.info("{}", employee);
log.info("-----------------");
log.info("Name: {}", employee.getName());
log.info("Code: {}", employee.getCode());
log.info("Department: {}", employee.getDepartment());
log.info("Skills: {}", employee.getSkills());
log.info("Addresses: {}", employee.getAddresses());
log.info("Status: {}", employee.getStatus());
log.info("Joining Date: {}", employee.getJoiningDate());
log.info("-----------------");
}
}
Findings
- Use
Setinstead ofListto fix the HibernateMultipleBagFetchException - Use field-based access
@Access(AccessType.FIELD)strategy why ?- Better readability of your code
- Omit getter or setter methods
- No need to mark utility methods as
@Transient
JPA Model for Document Structure Entity
https://semusings.dev/posts/2019/2019-11-18-jpa-model-for-document-structure-entity/