Introduction
Big-O notation, sometimes called asymptotic notation, is a mathematical notation that describes the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards a particular value or infinity.
In computer science, Big-O notation is used to classify algorithms according to how their running time or space requirements grow as the input size (n) grows. This notation characterizes functions according to their growth rates: different functions with the same growth rate may be represented using the same O notation.
Table of common time complexities
| Name | Complexity | Description |
|-------------------|---------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Constant Time | O(1) | Not dependent on the input data (n), the running time will always be the same. |
| Logarithmic Time | O(log n) | When it reduces the size of the input data in each step (it don’t need to look at all values of the input data). |
| Linear Time | O(n) | When the running time increases at most linearly with the size of the input data. |
| Quasilinear Time | O(n log n) | When each operation in the input data have a logarithm time complexity. |
| Quadratic Time | O(n^2) | When it needs to perform a linear time operation for each value in the input data. |
| Exponential Time | O(2^n) | When the growth doubles with each addition to the input data set. |
| Factorial Time | O(n!) | When it grows in a factorial way based on the size of the input data. |
Examples of common time complexities
public class ExamplesOfCommonTimeComplexities {
/*
Constant Time - O(1)
*/
public void constantTime(int a, int b) {
if (a > b)
System.out.println("A is greater than b.");
else
System.out.println("B is greater than a.");
}
/*
Logarithmic Time - O(log n)
*/
public void logarithmicTime(int[] a) {
int k = a.length / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
}
/*
Linear Time - O(n)
*/
public void linearTime(int[] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
}
/*
Quasilinear Time - O(n log n)
*/
public void quasilinearTime(int[] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
logarithmicTime(a);
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
}
/*
Quadratic Time - O(n^2)
*/
public void quadraticTime(int[] a, int[] b) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < b.length; j++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + "," + b[j] + " ");
}
}
}
/*
Exponential Time - O(2^n)
Example:
def fibonacci(n):
if n <= 1:
return n
return fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2)
*/
/*
Factorial Time - O(n!)
Example:
def heap_permutation(data, n):
if n == 1:
print(data)
return
for i in range(n):
heap_permutation(data, n - 1)
if n % 2 == 0:
data[i], data[n-1] = data[n-1], data[i]
else:
data[0], data[n-1] = data[n-1], data[0]
data = [1, 2, 3]
heap_permutation(data, len(data))
*/
}
Analyzing the time complexity of an algorithm
When analyzing the time complexity of an algorithm with several operations we need to describe the algorithm based on the largest complexity among all operations.
For Example: The algorithm to revers the orders of words
/*
Question - Given a string with multiple words and spaces represented as
a character array. Write an in-place algorithm to reverse the order of words
in the string.
Example:
CONVERT
['p', 'e', 'r', 'f', 'e', 'c', 't', ' ', 'm', 'a', 'k',
'e', 's', ' ', 'p', 'r', 'a', 'c', 't', 'i', 'c', 'e']
TO
['p', 'r', 'a', 'c', 't', 'i', 'c', 'e', ' ', 'm',
'a', 'k', 'e', 's', ' ', 'p', 'e', 'r', 'f', 'e', 'c', 't']
*/
public class ReverseWordInString {
/**
* @param a - an array
* @return - reverse character array by space
* <p>
* Time Complexity - O(n log n)
*/
public static char[] reverse(char[] a) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
char[] result = new char[a.length];
int startAt = 0;
for (int i = a.length - 1; i > -1; i--) {
if (a[i] != ' ') {
stack.push(a[i]);
}
boolean isComma = a[i] == ' ';
if (isComma || i == 0) {
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
result[startAt++] = stack.pop();
}
if (isComma) {
result[startAt++] = a[i];
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
Let’s analyze each operations:
- The for loop run from last index to first index i.e.
O(n). - Inside the for loop we have while loop that run till next
' 'from array of characters i.e.O(log n). - So, total time complexity of this for loop is
O(n log n). - Other operations have constant time complexity.
Now, for this algorithms we have O(n log n) is the largest complexity among all operations. Therefore, we can describe this algorithm has time complexity as O(n log n).
Big-O Cheat Sheet
The graph that shows running time complexity in terms of big-o notation. 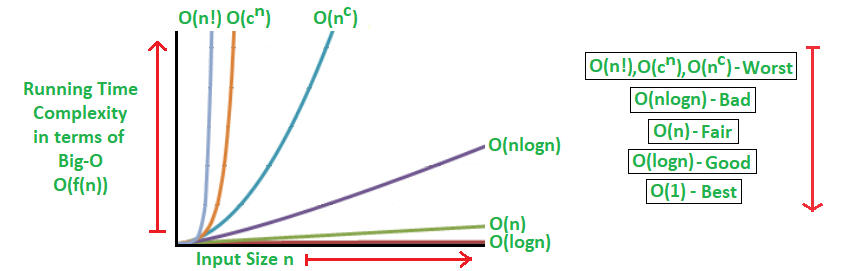
Here you can find a sheet with the time complexity of the operations in the most common data structures. 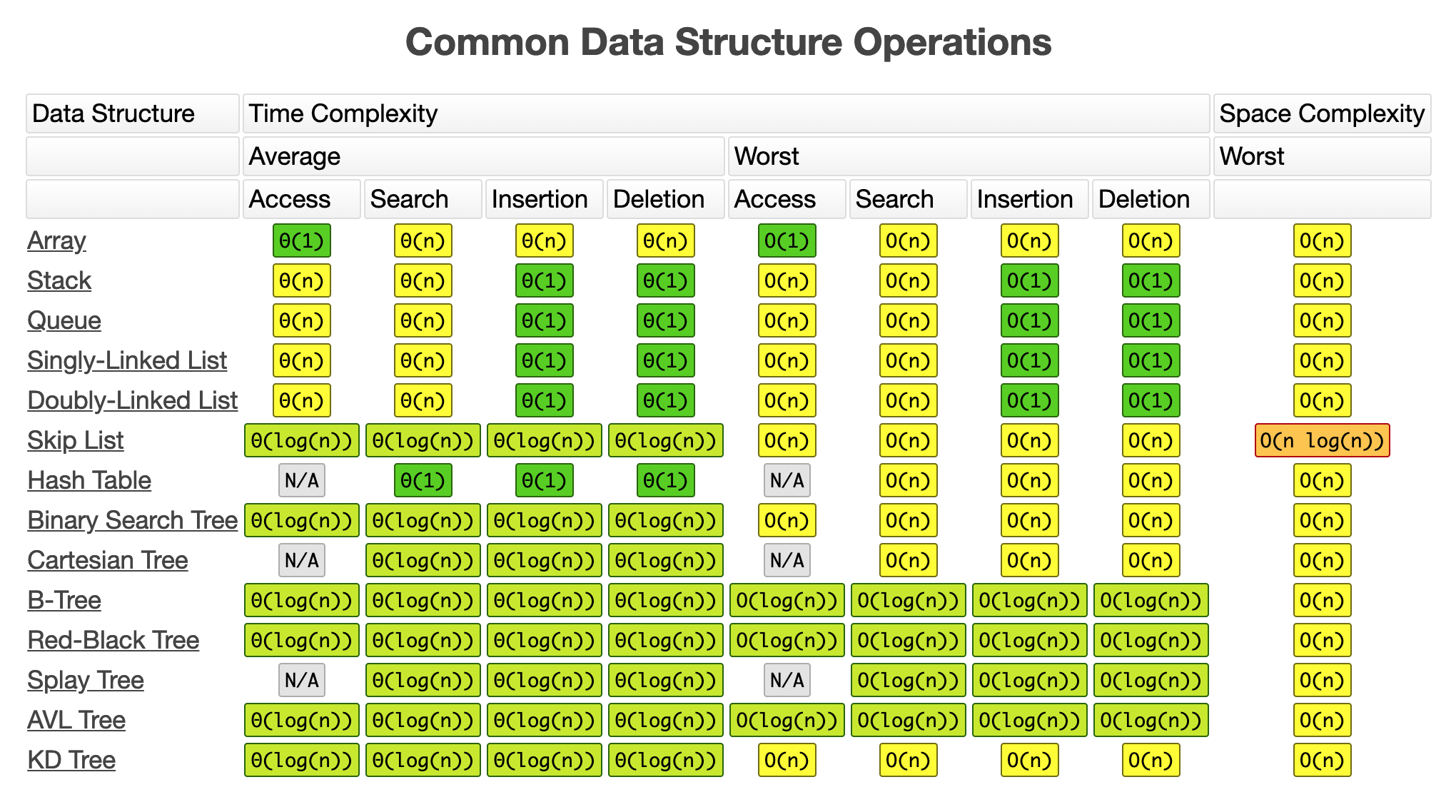
Here is another sheet with the time complexity of the most common sorting algorithms. 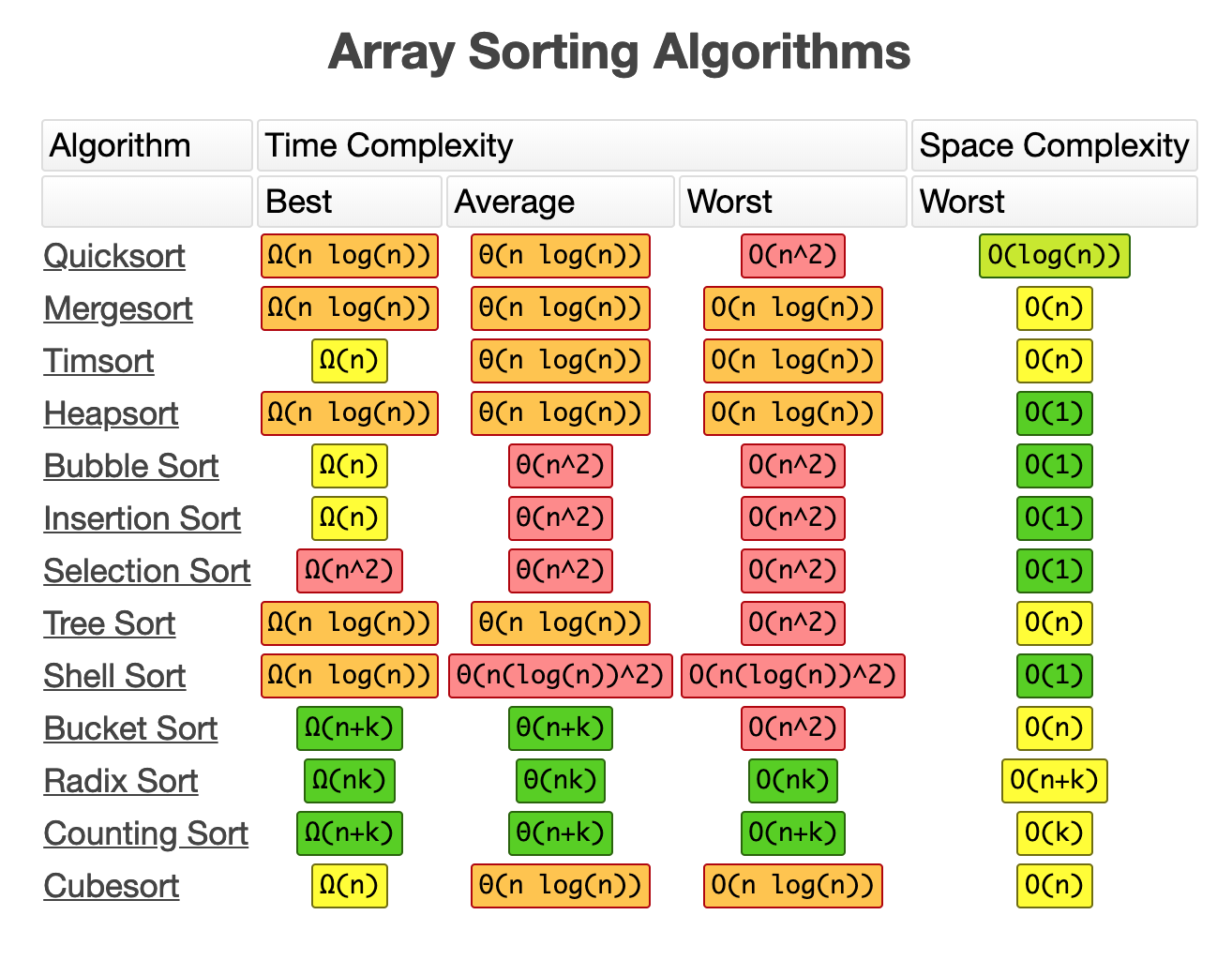
References
- Big-O notation: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Big_O_notation
- Big-O Cheat Sheet: https://www.bigocheatsheet.com/
